- Apr 25, 2015
- 1,846
- 2
- 2,203
- 327
Code:
$pshost = get-host
$pswindow = $pshost.ui.rawui
$newsize = $pswindow.buffersize
$newsize.height = 3000
$newsize.width = 3000
$pswindow.buffersize = $newsizeNow simply:
Code:
cd ~\DesktopTime to rip the list out:
Code:
Get-Process | Select Path | format-table -autosize > running.txtNow how about going to that Desktop, big boi?
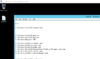
Just highlight everything underneath the Path --- stuff. This is what I have:
Code:
C:\Windows\system32\conhost.exe
C:\Windows\system32\dwm.exe
C:\Windows\system32\dwm.exe
C:\Windows\Explorer.EXE
C:\Windows\system32\LogonUI.exe
C:\Windows\system32\lsass.exe
C:\Windows\System32\msdtc.exe
C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe
C:\Windows\System32\rdpclip.exe
C:\Windows\system32\ServerManager.exe
C:\Windows\System32\spoolsv.exe
C:\Windows\system32\svchost.exe
C:\Windows\system32\svchost.exe
C:\Windows\System32\svchost.exe
C:\Windows\system32\svchost.exe
C:\Windows\system32\svchost.exe
C:\Windows\system32\svchost.exe
C:\Windows\system32\svchost.exe
C:\Windows\System32\svchost.exe
C:\Windows\System32\svchost.exe
C:\Windows\System32\svchost.exe
C:\Windows\system32\taskhostex.exe
C:\Windows\system32\wininit.exe
C:\Windows\system32\winlogon.exe
C:\Windows\system32\winlogon.exe
C:\Windows\system32\wbem\wmiprvse.exeNow you have a few options, at this point you can go use a "deduplicate list" tool online by copying/pasting or how about we go back into PowerShell and finish this like a real man?
Code:
gc .\running.txt | sort | Get-Unique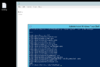
As we can see, this gives us:
Code:
C:\Windows\Explorer.EXE
C:\Windows\system32\conhost.exe
C:\Windows\system32\dwm.exe
C:\Windows\system32\LogonUI.exe
C:\Windows\system32\lsass.exe
C:\Windows\System32\msdtc.exe
C:\Windows\System32\rdpclip.exe
C:\Windows\system32\ServerManager.exe
C:\Windows\System32\spoolsv.exe
C:\Windows\System32\svchost.exe
C:\Windows\system32\svchost.exe
C:\Windows\System32\svchost.exe
C:\Windows\system32\svchost.exe
C:\Windows\system32\taskhostex.exe
C:\Windows\system32\wbem\wmiprvse.exe
C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe
C:\Windows\system32\wininit.exe
C:\Windows\system32\winlogon.exeConsider writing this to a file:
Code:
gc .\running.txt | sort | Get-Unique > uniq.txtNow let's say we want to grep this?
There is no "grep" on Windows, but there is findstr which is just about the same as grep. It's so similar I usually just alias the fucker.
How do we alias to use grep on Windows?
Code:
Set-Alias -Name grep -Value findstrExactly that way!
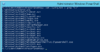
That's what I call boss mode mofo.
We can exfiltrate the data to termbin using "nc" simply do this:
Code:
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "https://eternallybored.org/misc/netcat/netcat-win32-1.12.zip" -OutFile "~\Desktop\nc.zip"Unzip this damn thing, since PowerShell is quite inconsistent and didn't have something so fuckin' basic early on.
Thanks for doing this in 5+ MicroShaft.
With this guy unzipped (Extract All...)
Copy "nc.exe" to C:\Windows
There we FUCKING go!
Code:
PS C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop> cat .\uniq.txt | grep "C:" | nc termbin.com 9999
https://termbin.com/p8ekExfiltrating tasklist, yeah h03z.
---
Keep in mind we can get hashes of all these:
Code:
Get-FileHash C:\Windows\system32\winlogon.exeNow if we had a hash database, we could perform comparisons against all running processes to known processes.
That sure would be nice, hmm? More to come.
Last edited: